Understanding How Tax Returns Are Calculated
Introduction
Tax returns play a crucial role in the financial lives of individuals and businesses alike. They serve as a mechanism for taxpayers to reconcile their income and deductions, ultimately determining the amount of tax they owe or are owed by the government. The process of calculating a tax return involves several steps and considerations that can greatly impact one’s financial situation. How tax return is calculated?
Income Calculation
Gathering Income Sources
The first step in calculating a tax return is to determine your total income for the year. This includes income from various sources such as wages, salaries, dividends, interest, rental income, and self-employment earnings. It’s essential to gather all relevant documents, such as W-2 forms and 1099s, to accurately report your income.
Differentiating Taxable and Non-Taxable Income
Not all forms of income are subject to taxation. Some types of income, like gifts, inheritances, and certain Social Security benefits, might be considered non-taxable. Understanding the distinction between taxable and non-taxable income is crucial to accurately calculating your tax liability.
Deduction and Credit Consideration
Itemized Deductions vs. Standard Deduction

Taxpayers have the option to either claim itemized deductions or take the standard deduction. Itemized deductions include expenses such as medical costs, mortgage interest, and charitable contributions. On the other hand, the standard deduction is a fixed amount that varies based on filing status. Choosing between itemized deductions and the standard deduction can significantly impact your tax liability.
Tax Credits
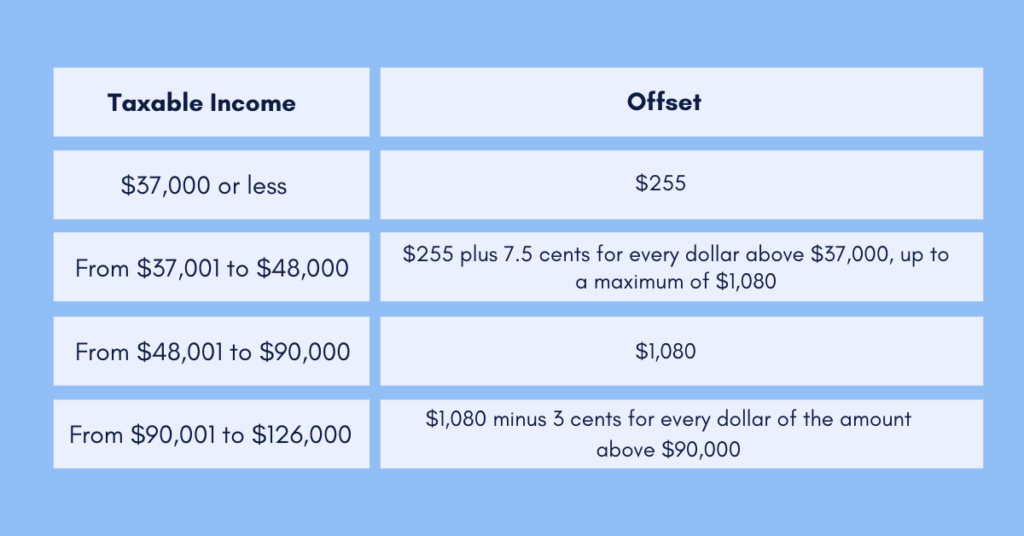
Tax credits directly reduce your tax liability on a dollar-for-dollar basis. Common tax credits include the Child Tax Credit, Earned Income Tax Credit, and education-related credits. It’s essential to carefully review the eligibility criteria for each credit and ensure you claim all the credits you’re eligible for, as they can significantly lower your tax bill.
Calculating Taxable Income and Tax Liability
Adjustments to Income
Before calculating your taxable income, you might be eligible to make certain adjustments, also known as above-the-line deductions. These deductions include contributions to traditional IRAs, student loan interest, and self-employment taxes. By subtracting these adjustments from your total income, you arrive at your adjusted gross income (AGI).
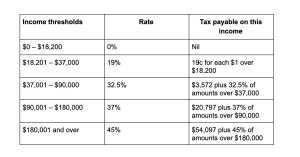
Tax Brackets and Rates
The federal tax system is structured into several tax brackets, each with its corresponding tax rate. As your income increases, you move into higher tax brackets with higher tax rates. The calculation involves applying the appropriate tax rate to your taxable income to determine your tentative tax liability. https://celestinos.com.au/best-sydney-tax-agent/
Applying Credits and Withholding
After determining your tax liability, you can offset it with any eligible tax credits. Additionally, if you had income tax withheld from your paychecks throughout the year, this amount is subtracted from your tax liability. The difference between your tax liability and your credits/withholding is your net tax due or refund.
Receiving a Refund or Making Payment
Refund
If your total tax payments and credits exceed your tax liability, you’re entitled to a tax refund. This is the government returning the excess amount you paid throughout the year. Many taxpayers eagerly await their refunds, which can be received via direct deposit or a mailed check.
Tax Payment
On the other hand, if your tax liability is higher than your total tax payments and credits, you will need to make a tax payment to cover the difference. Ensuring accurate calculations and proper withholdings can help avoid underpayment penalties and interest charges.
Conclusion
Calculating a tax return involves a complex interplay of income sources, deductions, credits, and tax rates. By understanding the various components and taking advantage of available deductions and credits, taxpayers can ensure they are accurately calculating their tax liability. Staying informed and seeking professional assistance when needed can lead to a smoother tax return process and potentially more favorable financial outcomes.