Australia’s taxation system is renowned for its complexity, and payroll taxation is no exception. As businesses navigate the intricacies of managing their finances, understanding payroll tax regulations is paramount. This guide delves into Australia’s approach to payroll taxation, providing insights into its intricacies and implications for businesses.
The Basics of Payroll Taxation in Australia
Payroll tax is a state-based tax levied on the wages a business pays to its employees. While the specifics vary across different states and territories, the underlying principles remain consistent. In Australia, businesses become liable for payroll tax when their total annual wages exceed a certain threshold set by each state or territory.
Thresholds and Rates
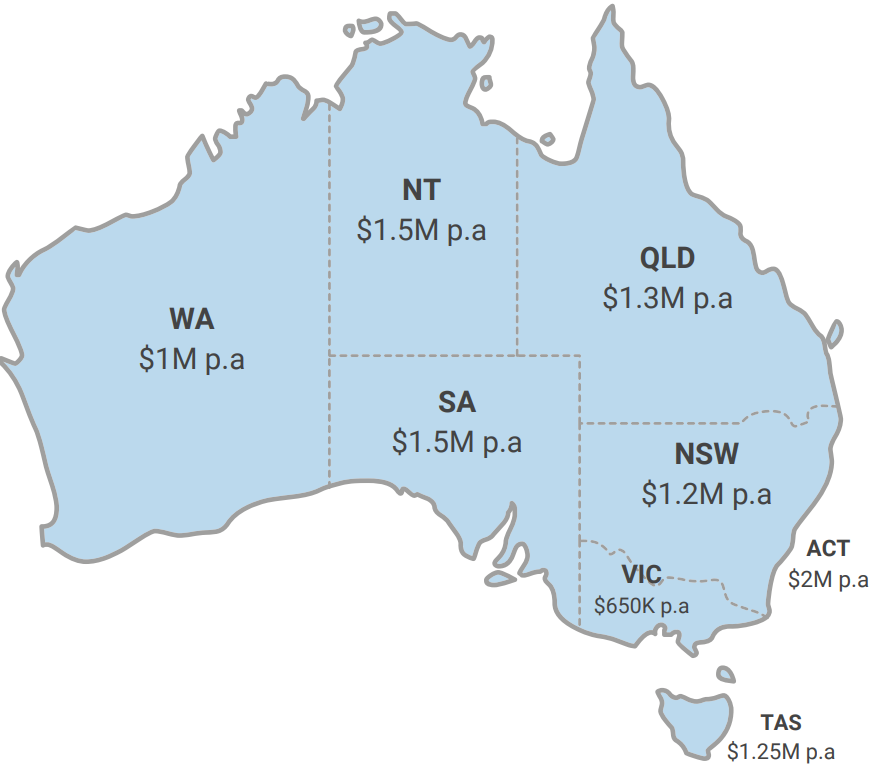
Each state and territory sets its own payroll tax threshold and rate. For instance, in New South Wales, the threshold for the 2023-24 financial year is $1 million in annual wages, while the rate is 5.45%. In contrast, Victoria has a threshold of $700,000 and a rate of 4.85%. It’s essential for businesses to stay updated on these thresholds and rates, as they may change annually.
Exemptions and Deductions
While businesses are required to pay payroll tax on most wages, certain exemptions and deductions apply. Common exemptions include wages paid to apprentices or trainees, wages paid to directors or shareholders who are not considered employees, and certain allowances and reimbursements. Additionally, businesses may be eligible for deductions related to wages paid to employees with disabilities or wages paid for interstate employees.

Compliance and Reporting
Ensuring compliance with payroll tax regulations is crucial for businesses to avoid penalties and fines. Businesses must register for payroll tax with the relevant state or territory revenue office and lodge periodic returns detailing their liable wages. These returns typically cover a specific period, such as a month or a quarter, and must be submitted within the designated timeframe.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite efforts to streamline payroll tax processes, businesses still encounter challenges in navigating its complexities. One common challenge is determining which wages are subject to payroll tax and which are exempt. Additionally, businesses operating across multiple states must contend with varying thresholds, rates, and compliance requirements, adding another layer of complexity.
Automation and Technology
As payroll tax compliance becomes increasingly intricate, many businesses are turning to automation and technology solutions to streamline processes and mitigate risks. Payroll software systems can help automate calculations, track changes in tax regulations, and generate accurate reports, reducing the burden on internal resources and enhancing compliance.
Conclusion
Australia’s approach to payroll taxation is multifaceted, encompassing diverse regulations, thresholds, and compliance requirements across different states and territories. For businesses, understanding and effectively managing payroll tax obligations are essential for financial sustainability and compliance. By staying informed, leveraging technology, and seeking expert guidance when needed, businesses can navigate the complexities of payroll taxation with confidence.